At the invitation of the top materials science journal Materials Today, the research team of Yuzhong Wang (an academician of CAE) of the College of Chemistry wrote and published a review "Recovery of Epoxy Thermosets and Their Composites", summarizing the current research development of the recovery of epoxy thermosets and their composites. Based on the research results of the team, the review puts forward suggestions on the use of recovery strategies and method terms, and summarizes the two recovery strategies of epoxy thermosets: source-based recovery strategy (SRS, rational design of recyclable thermosets) and end-based recovery strategy (ERS, recovery approaches of existing thermosets).
“As the currently predominant thermoset plastic, epoxy thermoset is widely used in composite materials, electronic packaging materials, coatings and adhesives. The rapid rise in epoxy thermoset composite materials used for wind turbine blades is largely driven byincreasing consumer demands for new energy sources such as wind power in the world. The recovery of the thermosetting polymers is among the most pressing contemporary challenges with the massive decommissioning of the materials. The review summarizes the recent advances on the recovery of epoxy thermosets from two different strategies including source-based recovery strategy (SRS, rational design of recyclable thermosets) and end-based recovery strategy (ERS, recovery approaches of existing thermosets). The recovery methods based on ERS are thoroughly discussed towards physcycling and chemcycling. We highlight important but easily neglected issues during the chemcycling, including mass transfer and heat transfer, solvent effects, full use of both reinforced materials and epoxy thermosets, as well as upcycling. It was pointed out that application-oriented chemcycling should be developed based on selective degradation and effective reconstruction. Finally, this review presents the forthcoming challenges and the prospects for future development.” (Abstract)
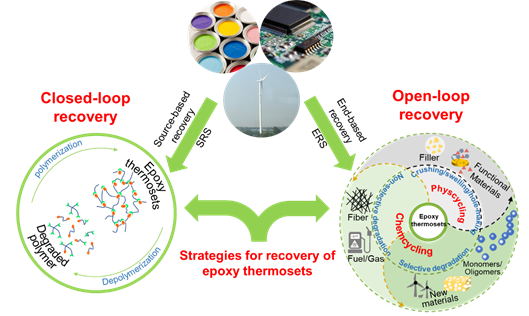
Epoxy thermosets have excellent mechanical properties, electrical insulation properties, adhesive properties and chemical stability. The increasing global demand for clean energy such as wind energy has promoted the production and application of epoxy thermoset, and the output of epoxy thermoset composites used for wind turbine blades has increased rapidly. How to realize green, efficient and high-value recycling of epoxy thermosets and their composites is a major challenge.
The paper was published in Materials Today (DOI: 10.1016/j.mattod.2022.12.005), with Sichuan University as the first work unit. Yuzhong Wang and Prof. Shimei Xu of the College of Chemistry are the corresponding authors of the paper, and Xu Zhao, a Class 2020 doctoral student is the first author. The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51721091), the 111 Plan (B20001), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2020SCUNL205), and the State Key Laboratory of Polymer Materials Engineering(sklpme2020-1-02).
