The research results of “Effect of Individualized, Family Involved Intervention Program on Elderly Patients with Non-cardiac Surgical Procedure” were recently published in JAMA Internal Medicine ( IF=20.768 ) in the form of original works. Being led by Professor Ji-rong Yue of Department of Geriatrics and National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics, West China Hospital, this research is a cooperative project with Harvard University. The results of this study put forward a more suitable personalized prevention strategy for postoperative delirium in elderly patients in China. The first author of this research paper is Yan-Yan Wang, a post-doctoral research fellow at the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics. Professor Ji-rong Yue is the corresponding author, and West China Hospital is the first work unit.

The MDT of the National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics, West China Hospital is the leader of this research project. After learning from Hospital Elder Life Program ( HELP ) of Professor Sharon K, Inouye at Harvard University, the research team has developed t-HELP ( tailored, family-involved HELP ) based on the cultural characteristics and current medical resources in China.
“Strengths of this study include involving family members to assist in delivering the t-HELP intervention. This novel approach may facilitate the adoption of HELP in other settings; tailoring of the menu of interventions received; customization of the protocols to maximize their effectiveness; addition of new protocols (eg, hypoxia, catheter-associated urinary tract infection); addition of anesthesiologists as interdisciplinary members involved in pain management; and rigorous evaluation, using a single-blind randomized clinical trial and sensitivity analyses, of the robustness of the findings to study dropouts.” ( Discussion )
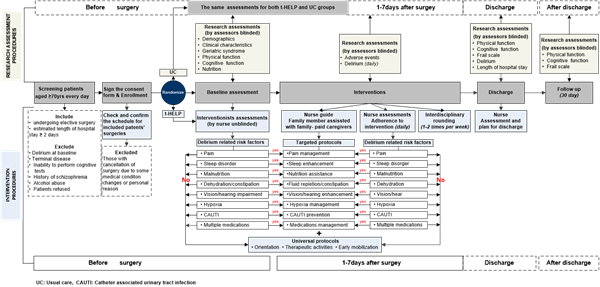
Figure 1. Study approach
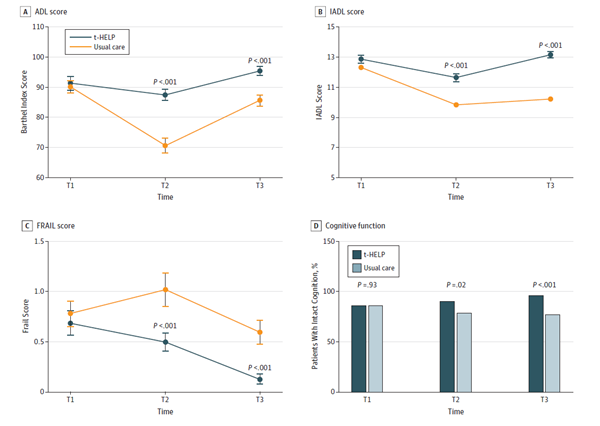
Figure 2.Change in Physical and Cognitive Function Over Time From Baseline to 30 Days After Discharge
A, The Barthel Index or activity of daily living ( ADL ) scores of patients in the usual care group were lower than those in the Tailored, Family-Involved Hospital Elder Life Program (t-HELP) group at discharge ( T2 ) and 30 days after discharge ( T3 ).
B, The instrumental activity of daily living ( IADL ) scores of patients in the usual care group were lower than those in the t-HELP group at T2 and T3.
C, The FRAIL ( Fatigue, Resistance, Ambulation, Illnesses, and Loss of Weight ) scale scores in the usual care group were higher than those in the t-HELP group at T2 and T3.
D, The proportion of intact cognition ( SPMSQ [Short Portable Mental Status Questionnaire] score) of patients in the t-HELP group was higher than that in the usual care group at T2 and T3. T1 indicates period before operation.”
This study has innovatively integrated family members or nursing workers to assist in the implementation of personalized intervention programs, providing evidence-based foundation for the global medical institutions with similar cultural background in the elderly individualized intervention programs and delirium prevention strategies. In the review titled “Including the Family in Perioperative Care of Older Adults—A Call for HELP” in the same edition of JAMA Internal Medicine, an expert points out that the American hospitals may need to learn from other cultures and include family members and nursing workers in the patient management program. The elderly patients who receive family care during the operation will have a strong sense of security in a strange hospital environment. Trust in family members or caregivers may be more effective in helping patients achieve early activity, as well as reducing anxiety and increasing sleep. In addition, family members can make use of their prior knowledge of the patient to enable him/her to actively participate in the rehabilitation process.
Article link: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamainternalmedicine/fullarticle/2753259?guestAccessKey=dbeb4823-8a79-49e8-bdf2-4db8a0ba950c&utm_source=jps&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=author_alert-jamanetwork&utm_content=author-author_engagement&utm_term=1m
