Zifeng Lin has made great progress in the research on both the preparation of two-dimensional MXenes based on vanadium and titanium and electrochemical energy storage. The research findings stem from his cooperation with Professor Patrice Simon fromInstitut Universitaire de France, Paris, France,and Qing Huang, a research fellow from Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Ningbo, China. Nature Materials has published the seminal research findings. Zifeng Lin,Patrice Simon and Qing Huangare the corresponding authors, and SCU College of Materials Science and Engineering is one of the corresponding work units.

“MXenes are mainly prepared from Al-containing MAX phases (where A = Al) by Al dissolution in F-containing solution; most other MAX phases have not been explored. Here a redox-controlled A-site etching of MAX phases in Lewis acidic melts is proposed and validated by the synthesis of various MXenes from unconventional MAX-phase precursors with A elements Si, Zn and Ga. A negative electrode of Ti3C2MXene material obtained through this molten salt synthesis method delivers a Li+storage capacity of up to 738 C g−1(205 mAh g−1) with high charge–discharge rate and a pseudocapacitive-like electrochemical signature in 1 M LiPF6carbonate-based electrolyte. MXenes prepared via this molten salt synthesis route may prove suitable for use as high-rate negative-electrode materials for electrochemical energy storage applications.” (Abstract)
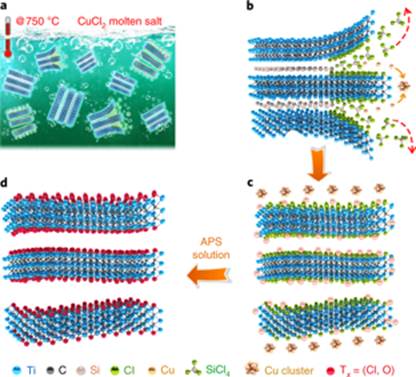
Fig. 1: Schematic of Ti3C2TxMXene preparation
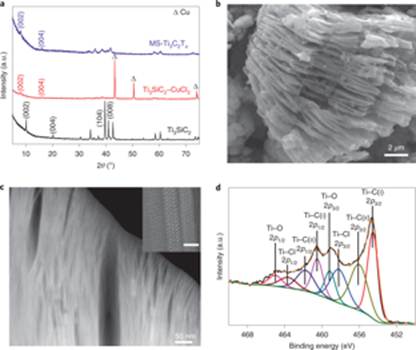
Fig. 2: Morphological and structural characterizations of MS-Ti3C2TxMXene
Zifeng Lin joined the Rare Earth Vanadium and Titanium Materials Center of the College of Materials Science and Engineering, Sichuan University in 2018. Under the leadership of Professor Ying Liu, he has been conducting research on vanadium and titanium resources in Panzhihua and Xichang areas. In recent two years, he has published papers in high-level academic journals such as Nature Materials、Nature Energy、Chemical Society Review、Advanced Functional Materials and Energy Storage Materials.
This study was supported financially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 21671195, 91426304, 51902320 and 51902319) and by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant no. 2018M642498), among others.
Article link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41563-020-0657-0
