In collaboration with the research team of Kelei Zhao from the Antibiotics Research and Re-evaluation Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province, Chengdu University,the research team of Zhaoming Su from the State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy of our university published a research paper entitled "Structural Basis of sRNA RsmZ Regulation of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Virus" online in Cell Research (IF: 46.351). In this study, the researchers analyzed the structure of full-length RsmZ combined with RsmA for the first time by using single-particle freeze electron microscopy, and revealed the molecular mechanism of its regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence.

In this study, three "clip" RsmA binding sites were identified by freeze electron microscopy. Using mutation and complement experiments, the researchers found that the complementary pairing of the stem-ring structure at the binding site was crucial for RsmZ to bind RsmA. By constructing RsmY/Z knockout strains and supplementing wild type and different mutant RsmZ, they verified that RsmZ regulated the expression of bacterial virulence related factors including biofilm formation, T6SS, QS, and affected downstream biofilm, chloromycetin production and other related phenotypes by forming complex three-dimensional structure combined with RsmA (Figure 1). Therefore, this study provides a structural biological basis for the development of targeted RNA drugs against bacterial drug resistance using Pseudomonas aeruginosa sRNA RsmZ as a new RNA target.
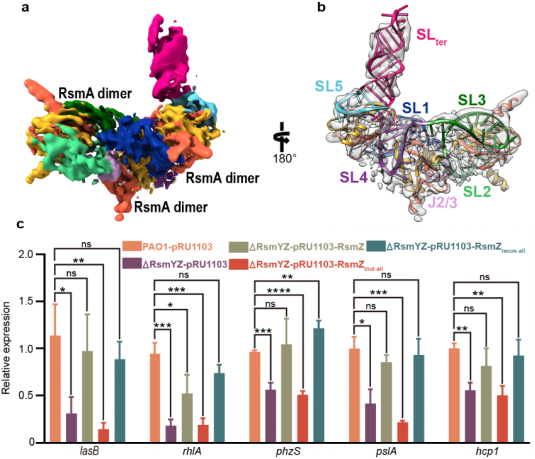
Fig. 1: Cryo-EM structures, RsmA binding affinity and regulation of WT and mutant RsmZ on gene expressions and phenotypes associated with P. aeruginos avirulence.
Xinyu Jia, Zhiling Pan(both doctoral students of the State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital ) and Yang Yuan(a doctoral student of the College of Life Sciences).Kelei Zhao and Zhaoming Suare the corresponding authors.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2022YFC2303700 and 2021YFA1301900 to Z.S.), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32222040 and 32070049 to Z.S., 31970131 to K.Z.), and Sichuan University start-up funding (20822041D4057 to Z.S.)and so forth.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-023-00786-3
