More than one million patients need blood purification to maintain their lives in China. This kind of cardiopulmonary bypass usually requires heparin, low molecular weight heparin and other anticoagulants to prevent thrombogenesis. However, the use of anticoagulants may lead to complications such as gastrointestinal bleeding and cerebral hemorrhage, which poses a serious threat to patients. How to balance the relationship between anticoagulation and bleeding has always been a major challenge in the field of blood purification.
After nearly three years of research, the team of Profs. Changsheng Zhao and Weifeng Zhao from the College of Polymer Science and Engineering(CPSE) first reported a pseudo-hemophilia anticoagulation strategy which ensures local, temporary and safe anticoagulation of blood purification cardiopulmonary bypass while avoiding bleeding risk of anticoagulants. The research findings are published in a paper entitled “Transient Blood Thinning During Extracorporeal Blood Purification via the Inactivation of Coagulation Factors by Hydrogel Microspheres” in Nature Biomedical Engineering. The corresponding authors are Prof. Weifeng Zhao and Prof. Changsheng Zhao. The first authors are Xin Song(an SCU alumnus and a doctoral student of the Imperial College London), Haifeng Ji(a doctoral student of CPSE) and Yupei Li(a doctoral student of the Department of Nephrology, West China Hospital).
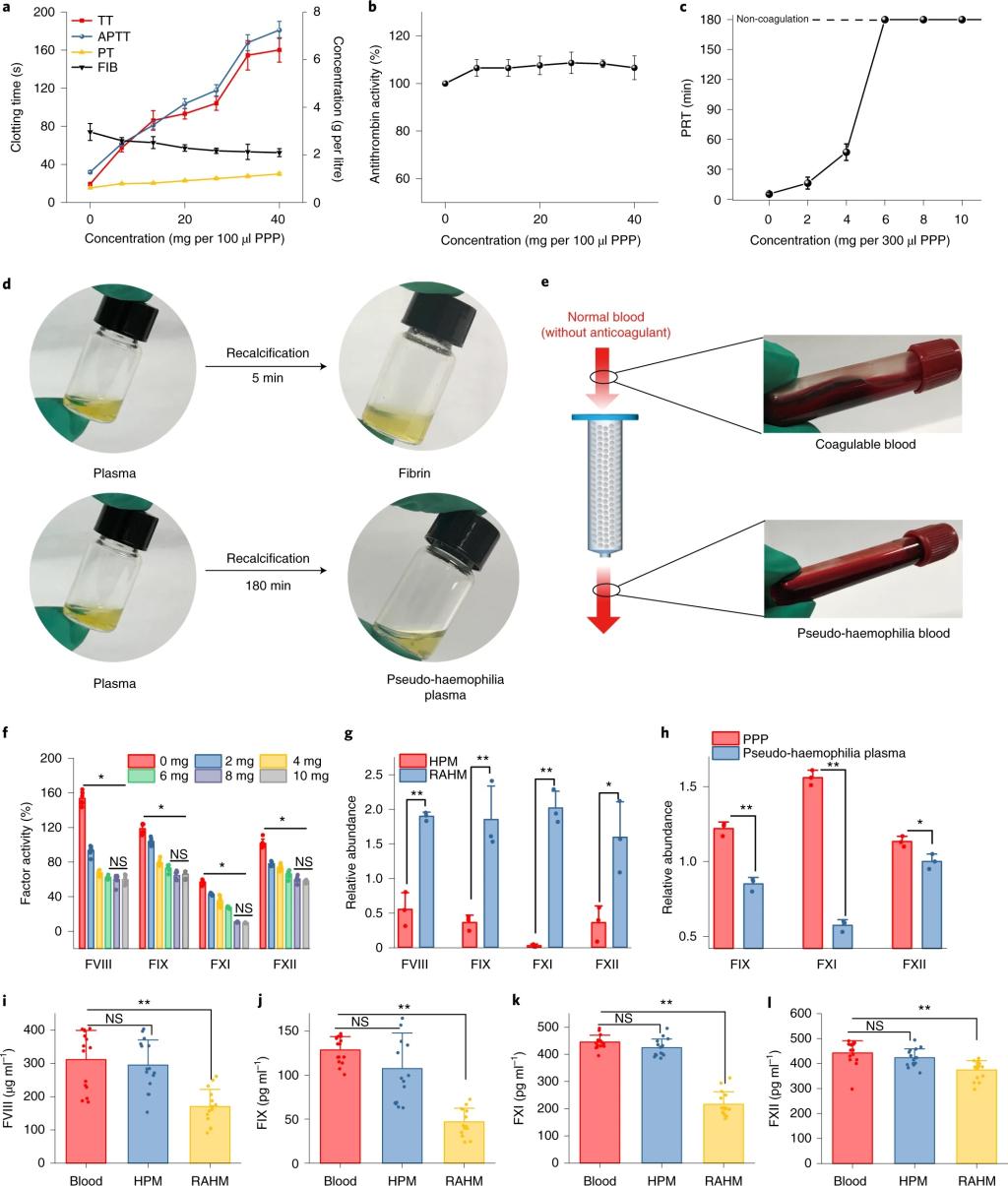
“Here, we show in vitro and in beagle dogs that hydrogel microspheres that adsorb the coagulation factors VIII, IX and XI provide transient blood thinning when placed in the extracorporeal circuit before blood purification. The microspheres inhibited the activities of the coagulation factors by levels (~8–30%) similar to those occurring in mild haemophilia. On its reintroduction into the animal, the purified pseudo-haemophilic blood favored faster recovery of haemostasis. The transient blood-thinning strategy may increase the safety of clinical blood-purification procedures.”(Abstract)
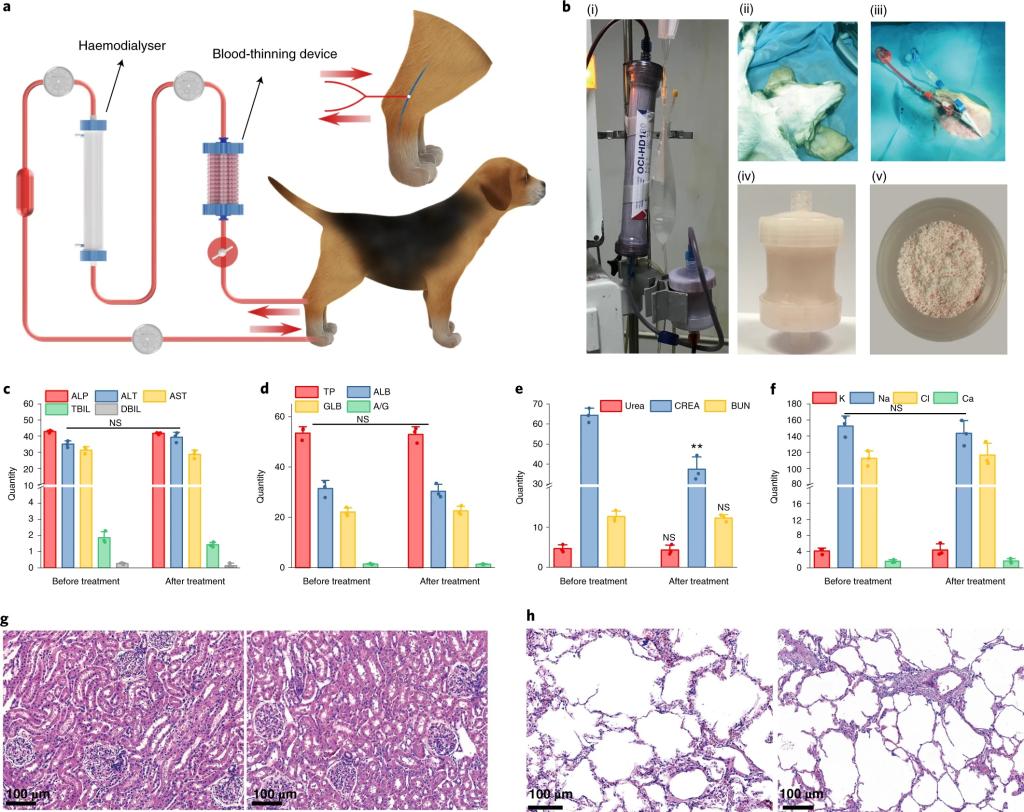
This anticoagulation strategy has been verified in a variety of in vitro blood purification treatments such as hemodialysis and hemoperfusion. It is of great significance for the design of anticoagulant materials, the miniaturization of the blood purification device, the innovation of the next generation filter, the simplification of blood purification process and the development of wearable artificial kidney in the future.
Article link:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41551-020-00673-x
