The research team of Professor Xun Sun and Ling Zhang published a research paper entitled "The Pore Size of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Regulates Their Antigen Delivery Efficiency" online in Science Advances on June 17. It was discovered thatMSNs with larger pore size showed stronger immune activation and antitumor efficacy than MSNs with smaller pore size.The first author of this paper is Xiaoyu Hong, a doctoral student of West China School of Pharmacy; the corresponding authors are Prof. Xun Sun of West China School of Pharmacy and Ling Zhang, an associate researcher of the College of Polymer Science and Engineering.
“Subunit vaccines generally proceed through a 4-step in vivo cascade—the DUMP cascade—to generate potent cell-mediated immune responses: (1) drainage to lymph nodes; (2) uptake by dendritic cells (DCs); (3) maturation of DCs; and (4) Presentation of peptide-MHC I complexes to CD8+ T cells. How the physical properties of vaccine carriers such as mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) influence this cascade is unclear. We fabricated 80-nm MSNs with different pore sizes (7.8 nm, 10.3 nm, and 12.9 nm) and loaded them with ovalbumin antigen. Results demonstrated these MSNs with different pore sizes were equally effective in the first three steps of the DUMP cascade, but those with larger pores showed higher cross-presentation efficiency (step 4). Consistently, large-pore MSNs loaded with B16F10 tumor antigens yielded the strongest antitumor effects. These results demonstrate the promise of our lymph node-targeting large-pore MSNs as vaccine-delivery vehicles for immune activation and cancer vaccination.” (Abstract)
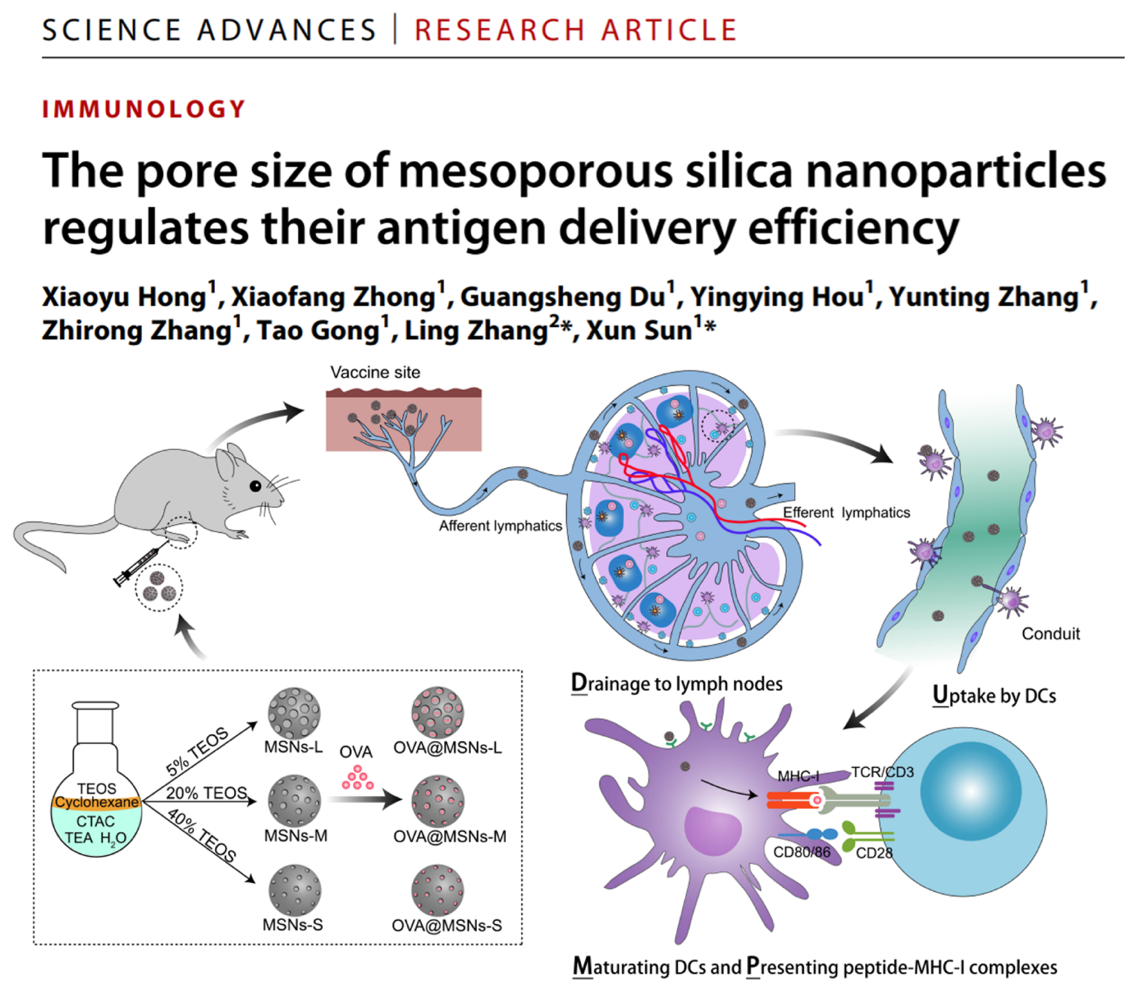
Schematic illustration of the DUMP cascade of antigen-loaded lymph node–targeting MSNs to induce adaptive immune response
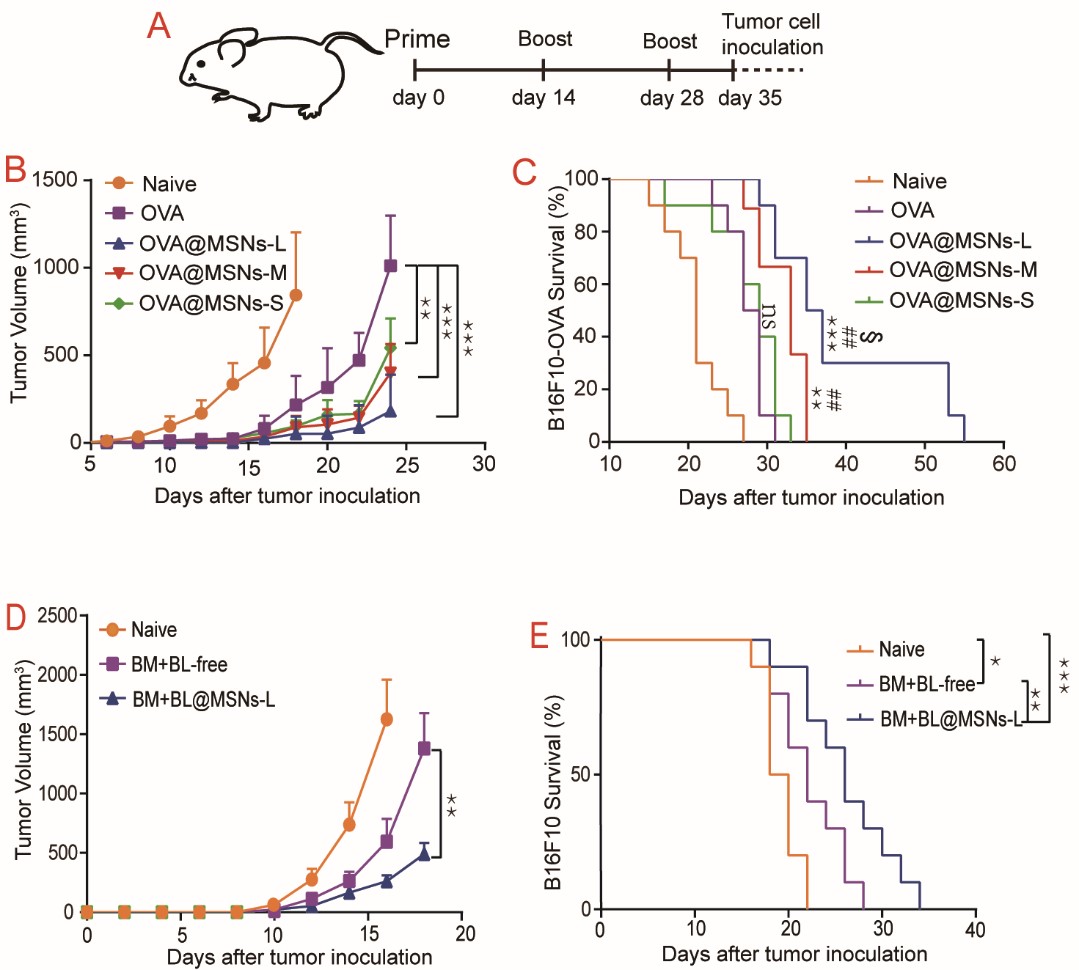
Tumor growth inhibition potency of MSN loading antigen and survival curve of mice
MSNs can deliver tumor antigens and induce antitumor immunity, which also proves that MSNs has great prospects in vaccine delivery. This research is supported by funding from the National Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars and Sichuan Province Major Science and Technology Projects.
Article link: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/6/25/eaaz4462/tab-pdf
